A little internet: Difference between revisions
| (9 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<span class="author">「 Loes Bogers, Anja Groten, Karl Moubarak 」</span> | <span class="author">「 Loes Bogers, Anja Groten, Karl Moubarak 」</span> | ||
The project 'Prototypes for a lighter internet' describes a collaborative exploration across the Netherlands and Armenia that resulted in a two week-long workshop for kids and teenagers at The TUMO Center for Creative Technologies<ref>https://tumo.org/</ref> in Yerevan – a free-of-charge educational program that puts teens in charge of their own learning. | The project ''Prototypes for a lighter internet'' describes a collaborative exploration across the Netherlands and Armenia that resulted in a two week-long workshop for kids and teenagers at The TUMO Center for Creative Technologies<ref>https://tumo.org/</ref> in Yerevan – a free-of-charge educational program that puts teens in charge of their own learning. | ||
<div class="smaller-image"> | <div class="smaller-image"> | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
The aim of the project was to pay attention to the challenges that come with building and participating in contemporary internet culture in a manner that is sustainable and equitable. Data centers, cable networks, always-on devices (e.g. routers and phones) that allow us to be connected via the Internet have huge energy requirements. Moreover, the mining required to source materials for required chips inside our hardware is exhausting the earth and is the cause for geopolitical tensions. With Prototypes for a | The aim of the project was to pay attention to the challenges that come with building and participating in contemporary internet culture in a manner that is sustainable and equitable. Data centers, cable networks, and always-on devices (e.g. routers and phones) that allow us to be connected via the Internet have huge energy requirements. Moreover, the mining required to source materials for required chips inside our hardware is exhausting the earth and is the cause for geopolitical tensions. With ''Prototypes for a lighter internet'', we took a hands-on approach to exploring the social and environmental implications of internet technologies from the perspective of those who will be most affected by the rising threats of climate change – kids and youngsters. | ||
<div class="smaller-image"> | <div class="smaller-image"> | ||
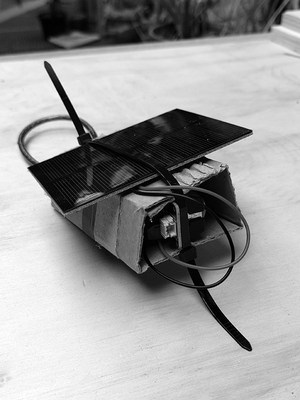
[[File:IMG_20220507_131336.png|thumb|alt=Mini internet package: | [[File:IMG_20220507_131336.png|thumb|alt=Mini internet package: ESP wifi module with rechargeable battery and mini solar panel|Mini internet package: ESP wifi module with rechargeable battery and mini solar panel]] | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
=== Our collaborative mission! === | === Our collaborative mission! === | ||
Participants joined the H&D collective for two weeks for an intensive research trajectory and worked together on developing prototypes for a lighter, less wasteful internet. The learning lab was process-driven, giving space for playful trial and error, guided by hacking principles<ref>We refer to hacking as the curious and joyful act of opening up technology, and using it in novel unexpected ways.</ref> | Participants joined the H&D collective for two weeks for an intensive research trajectory and worked together on developing prototypes for a lighter, less wasteful internet. The learning lab was process-driven, giving space for playful trial and error, guided by hacking principles.<ref>We refer to hacking as the curious and joyful act of opening up technology, and using it in novel, unexpected ways.</ref> The question we researched is: | ||
<blockquote> | <blockquote> | ||
"Why is the internet so heavy? <br> | "Why is the internet so heavy? <br> | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
</blockquote> | </blockquote> | ||
Through hands-on prototyping we worked our way towards building and imagining a lighter, less wasteful internet, and explored the limits and unexpected possibilities of such a small internet. | Through hands-on prototyping we worked our way towards building and imagining a lighter, less wasteful internet, and explored the limits and unexpected possibilities of such a small internet. | ||
Along the way we proposed many exercises to | Along the way, we proposed many exercises to reduce kb, and traced every step of the collaborative research project, documented successful and failed experiments, to share with each other and the world. | ||
<div class="smaller-image"> | <div class="smaller-image"> | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
=== Outcomes === | === Outcomes === | ||
We made a series of prototypes for a lighter internet consisting of: | We made a series of prototypes for a lighter internet, consisting of: | ||
* Energy-efficient local network for TUMO | * Energy-efficient local network for TUMO | ||
* Websites that are programmed with efficiency, accessibility and low bandwidth in mind | * Websites that are programmed with efficiency, accessibility and low bandwidth in mind | ||
* Low-res digital imagery that communicate 'more with less' bytes, that can be used on the web as well as in print | * Low-res digital imagery that communicate 'more with less' bytes, that can be used on the web as well as in print | ||
* Collaborative code documentation | * Collaborative code documentation | ||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
=== Tooling Days === | === Tooling Days === | ||
Participants could choose one of three "tooling tracks" that they could | Participants could choose one of three "tooling tracks" that they could followed for two days at the beginning of the curriculum: | ||
# Small images, compression, low-res graphics | # Small images, compression, low-res graphics | ||
# Accessible and sustainable approaches to HTML, CSS and JS | # Accessible and sustainable approaches to HTML, CSS and JS | ||
# Building the required hardware and connecting the | # Building the required hardware and connecting the toolchain | ||
The skills and knowledge acquired within these tracks were then brought together within group projects. | The skills and knowledge acquired within these tracks were then brought together within group projects. | ||
<span class="page-break"> </span> | |||
<div class="smaller-image"> | <div class="smaller-image"> | ||
| Line 53: | Line 55: | ||
=== Miscellaneous Exercises === | === Miscellaneous Exercises === | ||
'''Field day: mapping the physical internet''' | |||
We wanted to draw the attention | We wanted to draw the participants' attention to the physical presence of the internet in the building within which the workshop took place as well as the neighboring public spaces. This exercise consisted of gathering images, drawings and all forms of data showing where and how the internet reveals itself: WiFi routers, Ethernet cables, man-holes, connected devices, security cameras, rental bikes, WiFi names, etc... After some negotiation and reassuring – and handing in our phones – we also got to take a peek inside the server room. | ||
This exercise | This exercise created an active acknowledgment of the physicality of the internet, grounded the metaphorical cloud in physical hardware devices and brought awareness to things that were not (yet) networked. | ||
<div class="smaller-image"> | <div class="smaller-image"> | ||
| Line 63: | Line 65: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
'''Alt-text''' | |||
We explored Alt-texts, image descriptions or [ID], which are a detailed description of images that provide textual access to visual content. Alt-text also refers to the alt attribute in | |||
We explored Alt-texts, which are detailed image descriptions or [ID], which are a detailed description of images that provide textual access to visual content. Alt-text also refers to the alt attribute in HTML which is a common place to store them. | |||
<code><img src=”link” alt=”text goes here”></code> | <code> <img src=”link” alt=”text goes here”> </code> | ||
'''Exercise: [ID] Swap''' | '''Exercise: [ID] Swap''' | ||
Participants chose an image and wrote a detailed image description for it. They then swapped the description with the person sitting across from them, who searched for an image online that resembles the description. In the following they showed each other the images and discussed similarities and differences, objectivity and subjectivity of writing these | Participants chose an image and wrote a detailed image description for it. They then swapped the description with the person sitting across from them, who searched for an image online that resembles the description. In the following, they showed each other the images and discussed similarities and differences, objectivity and subjectivity of writing these descriptions. An interesting aspect about writing image descriptions and alt text is that you can add intention into it. | ||
It doesn’t necessarily make sense to go from left to right | It doesn’t necessarily make sense to go from left to right describing everything in an image because that might lose the central message or create disorientation. How to write a good image description? The '''object''' is the main focus. The '''action''' describes what is happening, usually what the object is doing. The '''context''' describes the surrounding environment. | ||
'''Exercise: Audio Auditing''' | '''Exercise: Audio Auditing''' | ||
As a screen reader describes a website participants draw the navigation and user flow of the website. | As a screen reader describes a website, participants draw the navigation and user flow of the website. | ||
This exercise activates an awareness of the too-often neglected software-aided navigation of websites through screen readers. This reverse-engineering of a website's design by listening to a screen reader | This exercise activates an awareness of the too-often neglected software-aided navigation of websites through screen readers. This reverse-engineering of a website's design by listening to a screen reader describing it brings to light the alternative, linear, and tree-like structure scraped out by the browser. | ||
'''Network observatory''' | |||
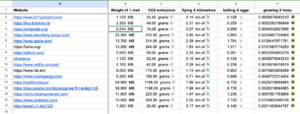
Together we used network inspection, observation and auditing tools to create an incomplete database of our favorite websites and their carbon footprints. We made use of tools for | Together we used network inspection, observation and auditing tools to create an incomplete database of our favorite websites and their carbon footprints. We made use of tools for trace routing, carbon-footprint measurement and data-bending to situate our network traffic in geographic, physical and political grounds. Although our database is small and focuses on the carbon offset of one visit to each of the websites, we also propose to see the problem more holistically and from a wider perspective: who is responsible for these emissions, and how could they use these arbitrary numbers like these do to reduce them? What is the responsibility of the individual website visit, and what is missing from these formulas? What if action were taken more collectively? | ||
[[File:Network-observatory.png|thumb]] | [[File:Network-observatory.png|thumb]] | ||
'''Throwing: Situated Deployment''' | |||
The most challenging part of the workshop | The most challenging part of the workshop as to think together about situations the prototypes could be deployed in. Following their hardware and software limitations of only being reachable within a 25-meter range, they are bound to their contexts in a radius of reach and representation. Although initially perceived as a limitation, it was this locality that informed the projects and their brainstorms. | ||
=== Prototypes === | === Prototypes === | ||
| Line 92: | Line 95: | ||
'''BusChat''' | '''BusChat''' | ||
by Diana, Emil, Sergey, Areg, Neron & Vahe | ''by Diana, Emil, Sergey, Areg, Neron & Vahe''<br> | ||
As first time visitors, we noticed that most bus stops in Yerevan don't provide much information about lines or bus schedules. | As first-time visitors, we noticed that most bus stops in Yerevan don't provide much information about lines or bus schedules. This is maybe one of the reasons we were offered to get around in cars we could request in an app called Yandex (the Russian equivalent to Uber). With this project, the students wanted to address a need for more information to make use of the public transport system by creating a mobile-first webpage that contains information on the bus routes, stops, and provides a message board to leave relevant updates. The page is specific to the buses operating on the big avenue outside of the TUMO center and would be hosted on a solar-powered module mounted somewhere on or near the bus stop. Students also wanted to offer people some games to play while waiting for the bus, that don't require a dataplan (because you can just log on to the local network to access it). | ||
<div class="smaller-image"> | <div class="smaller-image"> | ||
[[File:Buschat1.png|thumb|center|alt=Participant waiting at the bus stop outside of TUMO|Participant waiting at the bus stop outside of TUMO]] | [[File:Buschat1.png|thumb|center|alt=Participant waiting at the bus stop outside of TUMO|Participant waiting at the bus stop outside of TUMO]] | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="smaller-image"> | <div class="smaller-image"> | ||
[[File:Buschat2.png|thumb|center|alt=the BusChat on a mobile|The BusChat on a mobile]] | [[File:Buschat2.png|thumb|center|alt=the BusChat on a mobile|The BusChat on a mobile]] | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<span class="page-break"> </span> | |||
'''ParkGame''' | '''ParkGame''' | ||
by Tatev, Liana, Ani, Aram and Miqael | ''by Tatev, Liana, Ani, Aram and Miqael'' <br> | ||
TUMO Center looks out over a huge park with fountains next to the river. This group of students took inspiration from the projects we made in earlier workshops. Their hybrid game tells the story of a | TUMO Center looks out over a huge park with fountains next to the river. This group of students took inspiration from the projects we made in earlier workshops. Their hybrid game tells the story of a traveler who is lost from his tour group. To catch up with them, they have to find key codes hidden in the park and correctly answer questions about Armenia. To complete the game, players have to physically move around the park to find the 13 key codes, and enter them into their mobiles to continue to the 13 quiz questions. | ||
<div class="smaller-image"> | <div class="smaller-image"> | ||
[[File:Parkgame3.png|thumb|center|alt=Screenshot of one of the questions in the mobile game| | [[File:Parkgame3.png|thumb|center|alt=Screenshot of one of the questions in the mobile game|]] | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="smaller-image"> | <div class="smaller-image"> | ||
[[File:Parkgame1.png|thumb|center|alt= | [[File:Parkgame1.png|thumb|center|alt=Screenshots of one of the questions in the mobile game|Screenshots of one of the questions in the mobile game]] | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 125: | Line 126: | ||
<div class="smaller-image"> | <div class="smaller-image"> | ||
[[File:Parkgame2.jpeg|thumb|center|alt=Players looking for a code near a bench | [[File:Parkgame2.jpeg|thumb|center|alt=Players looking for a code near a park bench|Players looking for a code near a bench in the park]] | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<span class="page-break"> </span> | |||
'''Emergency Service''' | '''Emergency Service''' | ||
by | ''by Nane, Lilith, Marie, Robert, Harout & Mane''<br> | ||
After exploring the physical parts of the Internet it became clear that this infrastructure is inherently vulnerable and can be damaged. So what would we do if there | After exploring the physical parts of the Internet, it became clear that this infrastructure is inherently vulnerable and can be damaged. So what would we do if there was an earthquake and our infrastructure stopped working altogether? Where would people get information? How would they contact each other? This local network is designed to provide information and function as a message board where people can leave messages to let others know they need help. The students explained that such a service is extra relevant now, as the region of Artsakh - which has an ethnic Armenian population - is disputed territory and is currently blockaded by Azerbaijan, causing shortages of food, medicine and electricity for the 120,000 residents in the region. | ||
<div class="smaller-image"> | <div class="smaller-image"> | ||
[[File:Emergency.png|thumb|center|alt=The message board on a mobile phone|The message board on a mobile phone]] | [[File:Emergency.png|thumb|center|alt=The message board on a mobile phone|The message board on a mobile phone]] | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Latest revision as of 09:44, 19 October 2023
Prototypes for a lighter internet
The project Prototypes for a lighter internet describes a collaborative exploration across the Netherlands and Armenia that resulted in a two week-long workshop for kids and teenagers at The TUMO Center for Creative Technologies[1] in Yerevan – a free-of-charge educational program that puts teens in charge of their own learning.
The aim of the project was to pay attention to the challenges that come with building and participating in contemporary internet culture in a manner that is sustainable and equitable. Data centers, cable networks, and always-on devices (e.g. routers and phones) that allow us to be connected via the Internet have huge energy requirements. Moreover, the mining required to source materials for required chips inside our hardware is exhausting the earth and is the cause for geopolitical tensions. With Prototypes for a lighter internet, we took a hands-on approach to exploring the social and environmental implications of internet technologies from the perspective of those who will be most affected by the rising threats of climate change – kids and youngsters.
Our collaborative mission!
Participants joined the H&D collective for two weeks for an intensive research trajectory and worked together on developing prototypes for a lighter, less wasteful internet. The learning lab was process-driven, giving space for playful trial and error, guided by hacking principles.[2] The question we researched is:
"Why is the internet so heavy?
(And what can we do about it?)"
Through hands-on prototyping we worked our way towards building and imagining a lighter, less wasteful internet, and explored the limits and unexpected possibilities of such a small internet. Along the way, we proposed many exercises to reduce kb, and traced every step of the collaborative research project, documented successful and failed experiments, to share with each other and the world.
Outcomes
We made a series of prototypes for a lighter internet, consisting of:
- Energy-efficient local network for TUMO
- Websites that are programmed with efficiency, accessibility and low bandwidth in mind
- Low-res digital imagery that communicate 'more with less' bytes, that can be used on the web as well as in print
- Collaborative code documentation
The two-week long curriculum broke the question of creating prototypes for a lighter internet into smaller chunks and exercises.
Tooling Days
Participants could choose one of three "tooling tracks" that they could followed for two days at the beginning of the curriculum:
- Small images, compression, low-res graphics
- Accessible and sustainable approaches to HTML, CSS and JS
- Building the required hardware and connecting the toolchain
The skills and knowledge acquired within these tracks were then brought together within group projects.
Miscellaneous Exercises
Field day: mapping the physical internet
We wanted to draw the participants' attention to the physical presence of the internet in the building within which the workshop took place as well as the neighboring public spaces. This exercise consisted of gathering images, drawings and all forms of data showing where and how the internet reveals itself: WiFi routers, Ethernet cables, man-holes, connected devices, security cameras, rental bikes, WiFi names, etc... After some negotiation and reassuring – and handing in our phones – we also got to take a peek inside the server room.
This exercise created an active acknowledgment of the physicality of the internet, grounded the metaphorical cloud in physical hardware devices and brought awareness to things that were not (yet) networked.
Alt-text
We explored Alt-texts, which are detailed image descriptions or [ID], which are a detailed description of images that provide textual access to visual content. Alt-text also refers to the alt attribute in HTML which is a common place to store them.
<img src=”link” alt=”text goes here”>
Exercise: [ID] Swap
Participants chose an image and wrote a detailed image description for it. They then swapped the description with the person sitting across from them, who searched for an image online that resembles the description. In the following, they showed each other the images and discussed similarities and differences, objectivity and subjectivity of writing these descriptions. An interesting aspect about writing image descriptions and alt text is that you can add intention into it. It doesn’t necessarily make sense to go from left to right describing everything in an image because that might lose the central message or create disorientation. How to write a good image description? The object is the main focus. The action describes what is happening, usually what the object is doing. The context describes the surrounding environment.
Exercise: Audio Auditing
As a screen reader describes a website, participants draw the navigation and user flow of the website. This exercise activates an awareness of the too-often neglected software-aided navigation of websites through screen readers. This reverse-engineering of a website's design by listening to a screen reader describing it brings to light the alternative, linear, and tree-like structure scraped out by the browser.
Network observatory
Together we used network inspection, observation and auditing tools to create an incomplete database of our favorite websites and their carbon footprints. We made use of tools for trace routing, carbon-footprint measurement and data-bending to situate our network traffic in geographic, physical and political grounds. Although our database is small and focuses on the carbon offset of one visit to each of the websites, we also propose to see the problem more holistically and from a wider perspective: who is responsible for these emissions, and how could they use these arbitrary numbers like these do to reduce them? What is the responsibility of the individual website visit, and what is missing from these formulas? What if action were taken more collectively?
Throwing: Situated Deployment
The most challenging part of the workshop as to think together about situations the prototypes could be deployed in. Following their hardware and software limitations of only being reachable within a 25-meter range, they are bound to their contexts in a radius of reach and representation. Although initially perceived as a limitation, it was this locality that informed the projects and their brainstorms.
Prototypes
BusChat
by Diana, Emil, Sergey, Areg, Neron & Vahe
As first-time visitors, we noticed that most bus stops in Yerevan don't provide much information about lines or bus schedules. This is maybe one of the reasons we were offered to get around in cars we could request in an app called Yandex (the Russian equivalent to Uber). With this project, the students wanted to address a need for more information to make use of the public transport system by creating a mobile-first webpage that contains information on the bus routes, stops, and provides a message board to leave relevant updates. The page is specific to the buses operating on the big avenue outside of the TUMO center and would be hosted on a solar-powered module mounted somewhere on or near the bus stop. Students also wanted to offer people some games to play while waiting for the bus, that don't require a dataplan (because you can just log on to the local network to access it).
ParkGame
by Tatev, Liana, Ani, Aram and Miqael
TUMO Center looks out over a huge park with fountains next to the river. This group of students took inspiration from the projects we made in earlier workshops. Their hybrid game tells the story of a traveler who is lost from his tour group. To catch up with them, they have to find key codes hidden in the park and correctly answer questions about Armenia. To complete the game, players have to physically move around the park to find the 13 key codes, and enter them into their mobiles to continue to the 13 quiz questions.
Emergency Service
by Nane, Lilith, Marie, Robert, Harout & Mane
After exploring the physical parts of the Internet, it became clear that this infrastructure is inherently vulnerable and can be damaged. So what would we do if there was an earthquake and our infrastructure stopped working altogether? Where would people get information? How would they contact each other? This local network is designed to provide information and function as a message board where people can leave messages to let others know they need help. The students explained that such a service is extra relevant now, as the region of Artsakh - which has an ethnic Armenian population - is disputed territory and is currently blockaded by Azerbaijan, causing shortages of food, medicine and electricity for the 120,000 residents in the region.
- ↑ https://tumo.org/
- ↑ We refer to hacking as the curious and joyful act of opening up technology, and using it in novel, unexpected ways.