Earth battery: Difference between revisions
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
Make sure you take mud as well as some water (see image below). | Make sure you take mud as well as some water (see image below). | ||
==== Tools | ==== Tools ==== | ||
*Pot and stove to cook the agar mixture | *Pot and stove to cook the agar mixture | ||
*Multimeter | *Multimeter | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
*Breadboard | *Breadboard | ||
*Kitchen scale | *Kitchen scale | ||
*Liquids measuring cup | |||
*Tape (or anything to mark different wires) | |||
==== Materials | ==== Materials ==== | ||
*Mud | *Mud | ||
*Containers with | *Containers with wide opening on top (ex: glass jar or plastic container - around 1L) | ||
*Electric wires ( Copper wires 30 cm - 2 wires are needed per battery) | *Electric wires (Copper wires 30 cm - 2 wires are needed per battery) | ||
*Stainless steel grids to be cut in rectangles. Size : around 8 x 8 cm, but can change according to the size and shape of your container. Aluminium nets are good to use but they are less conductive. You can use also kitchen strainer mesh. You can also experiment with the size of the net, for example: making it like a strip 8 x 20, to have more surface area. In this case | *Stainless steel grids to be cut in rectangles. Size : around 8 x 8 cm, but can change according to the size and shape of your container. Aluminium nets are good to use but they are less conductive. You can use also kitchen strainer mesh. You can also experiment with the size of the net, for example: making it like a strip 8 x 20, to have more surface area. In this case you can roll it without making the surfaces touch. | ||
*Epoxy glue | *Epoxy glue | ||
*Small brush to spread the glue | *Small brush to spread the glue | ||
*Active coal | *Active coal | ||
*Agar ( | *Agar (10g is needed per 1L battery) | ||
* | *Salt substances (any broth powder - 1 pack, 2g per battery). Broth powder is the one you use for cooking. We used the veggie broth cubes that you buy from the supermarket. | ||
*LED | *LED | ||
*Drinking Water | *Drinking Water | ||
==== Making the Cathodes ==== | ==== Making the Cathodes ==== | ||
| Line 38: | Line 37: | ||
[[File:cathode1.jpg|ID: Hands performing the steps described in what follows]] | [[File:cathode1.jpg|ID: Hands performing the steps described in what follows]] | ||
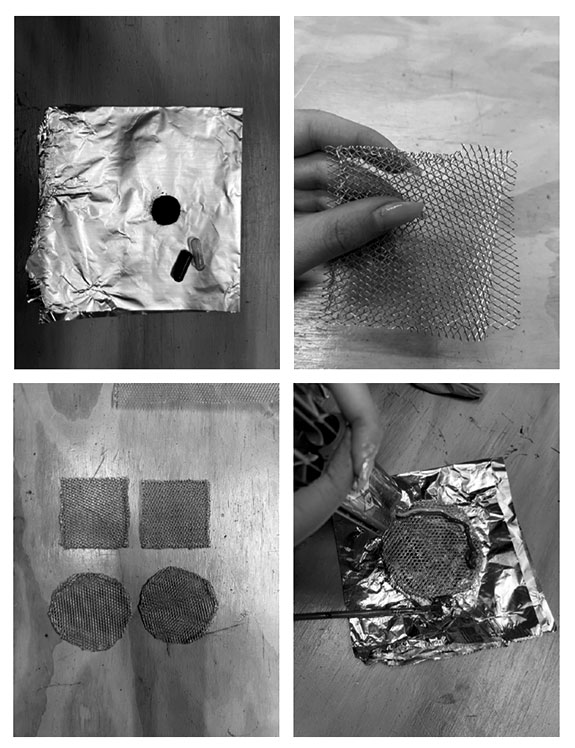
# | #Empty the pills of the active coal to get the powder out, and place it on a sheet. (about 10 pills powder per 1 cathode disc) | ||
#Cut two meshes in a rectangular shape 8 x 8cm. Place them in opposite directions and fold the edges so they are attached. We make two layers so it can hold the glue and coal well. | |||
# | #Brush the glue on the mesh and make sure that you add enough glue and that it is brushed evenly on the surface of the mesh. | ||
# | |||
[[File:cathode2.jpg|ID: Hands performing the steps described in what follows]] | [[File:cathode2.jpg|ID: Hands performing the steps described in what follows]] | ||
#Cover the brushed | #Cover the brushed mesh with the active coal powder and press it very well. After pressing, add coal and press again. It is very important that the coal is covering the whole surface. | ||
#After making sure that the mesh is covered and pressed with coal, connect the mesh from one of the sides to an electric wire. At the end you might need to bend the mesh to fit your container. Bend it, but be sure not to make the edges touch each other. More coal surface is better! Now leave it to fully dry. | |||
#After making sure that | |||
==== Preparing first part of the Soil Battery ==== | ==== Preparing first part of the Soil Battery ==== | ||
| Line 55: | Line 51: | ||
[[File:cathode3.jpg|ID: 1. The finished cathode, 2. Two glass jars half filled with mud, with a wire from the cathode coming out of the opening]] | [[File:cathode3.jpg|ID: 1. The finished cathode, 2. Two glass jars half filled with mud, with a wire from the cathode coming out of the opening]] | ||
#Put the cathode in the container (make sure that the glue dried and the coal is stuck to it). | |||
#Fill the jar with mud so it covers the cathode, keeping the wire out of the container. | |||
Mark the wire with tape to identify that its negative. (black = negative) | #Mark the wire with tape to identify that its negative. (black = negative) | ||
#Hit the container to get all the trapped air bubbles out. It is VERY IMPORTANT to release the air bubbles from the mud. | |||
==== Making the proton exchange membrane ==== | ==== Making the proton exchange membrane ==== | ||
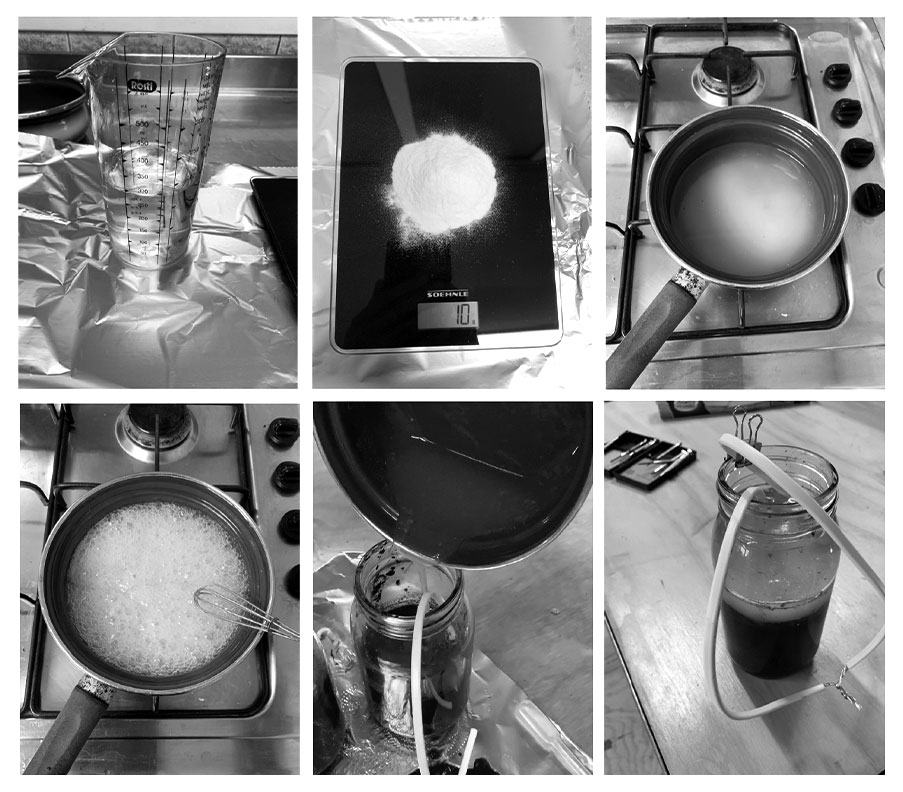
[[File:mudbattery_parallel.jpg|ID: Process of preparing and pouring the agar described in the steps below | [[File:mudbattery_parallel.jpg|ID: Process of preparing and pouring the agar described in the steps below]] | ||
]] | |||
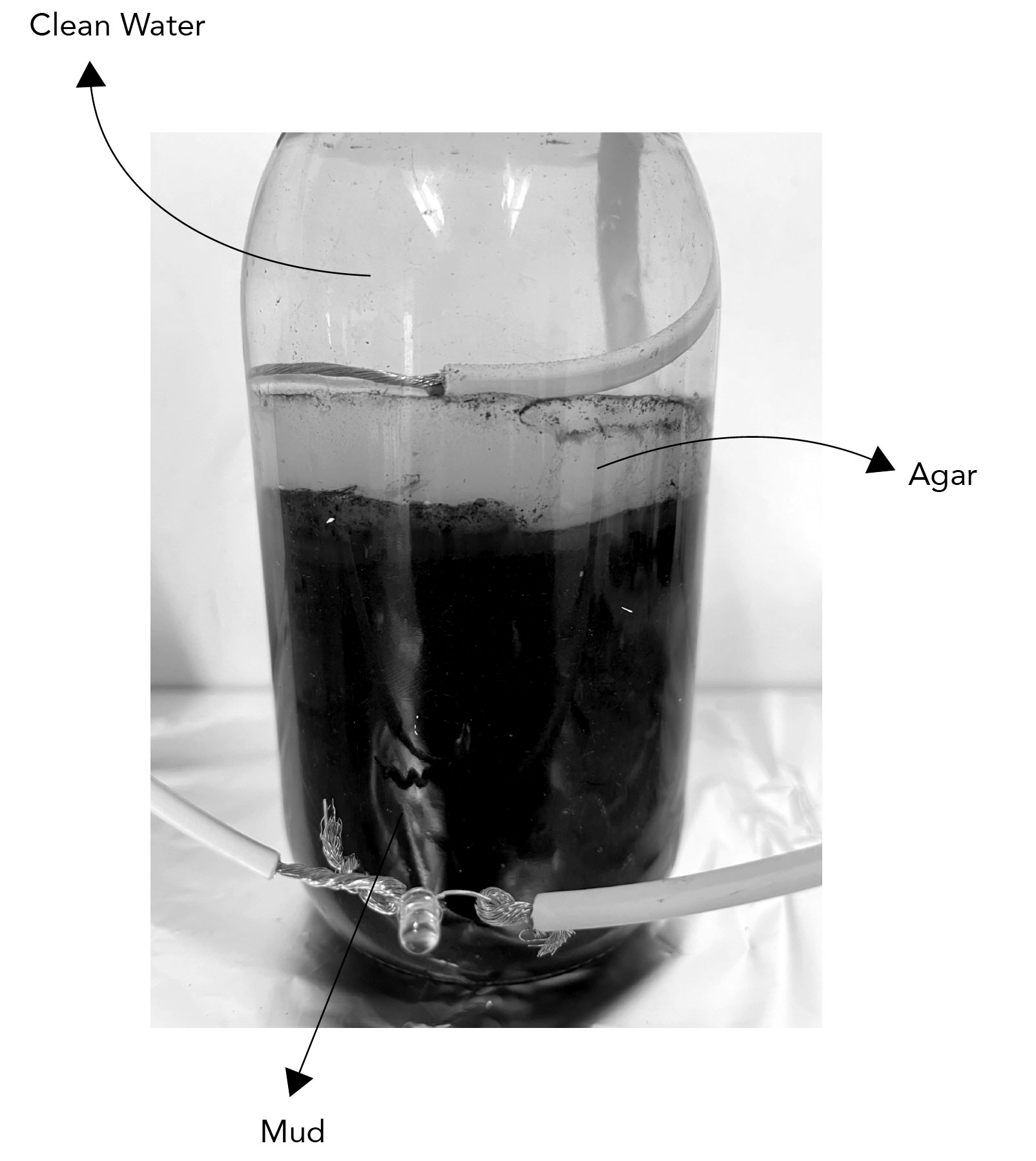
[[File:battery_demonstration.jpg|ID: Mud battery in a glass jar: half filled with mud, then a layer of solidified agar, and filled to the top with clean tap water. Two cables are coming from the jar and are connected to an LED for illustration purposes.]] | [[File:battery_demonstration.jpg|ID: Mud battery in a glass jar: half filled with mud, then a layer of solidified agar, and filled to the top with clean tap water. Two cables are coming from the jar and are connected to an LED for illustration purposes.]] | ||
==== Connecting the batteries in parallel ==== | ==== Connecting the batteries in parallel ==== | ||
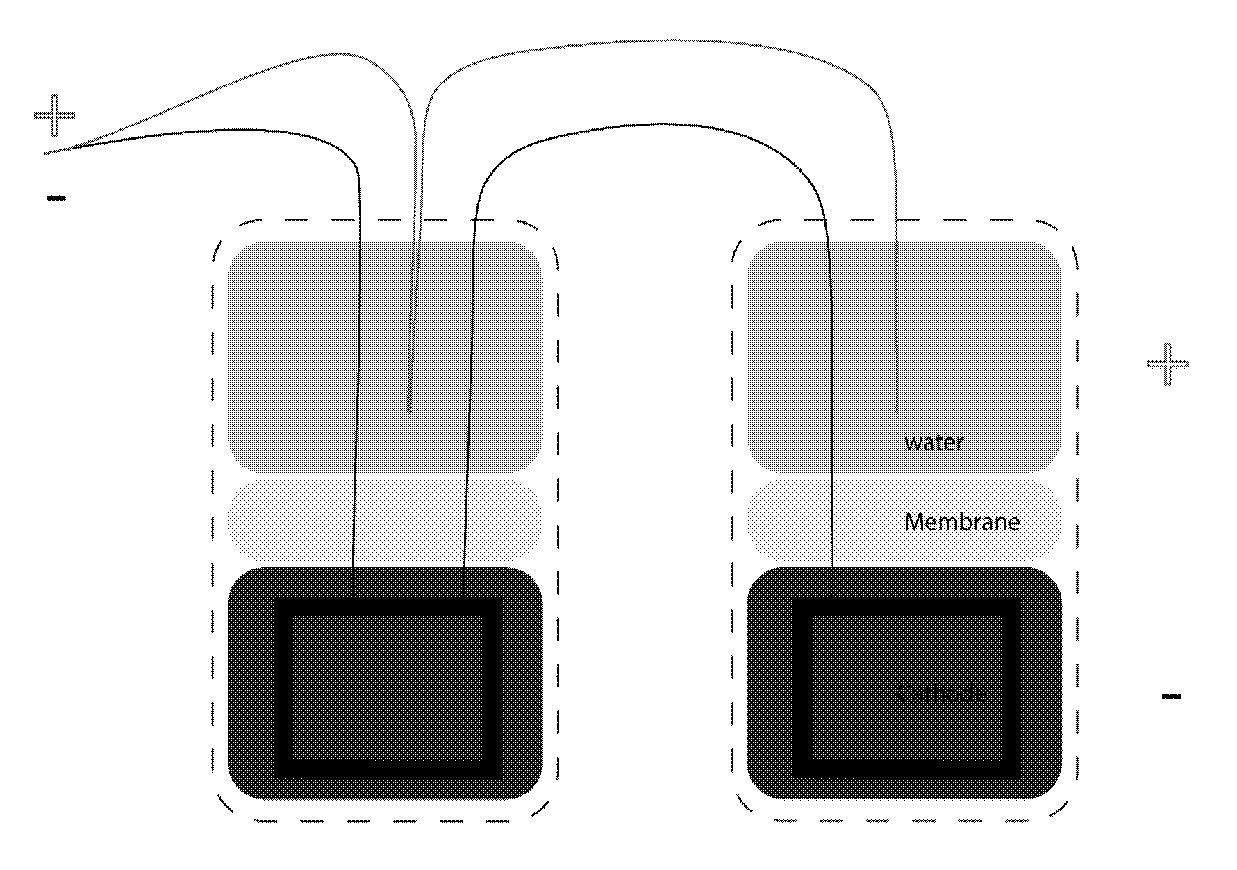
The water part in the battery is (+) and the mud part is (-). When connecting two batteries in | The water part in the battery is (+) and the mud part is (-). When connecting two batteries in parallel the (-) from the first battery should be connected to the (-) in the second one, and the (+) from the first to the (+) in the second. Then the (-) and (+) should be connected together to close the circuit. See the drawing: | ||
[[File:agar_membrane.jpg| | [[File:agar_membrane.jpg|ID: Diagram of two mud batteries connected in parallel: The cathode (or minus, black) comes from the mud of battery one and is connected to the cathode of battery 2. The anode (or plus, red) is the wire sitting in the top half in the water, and is connected to the anode of battery two.]] | ||
The mud-batteries how-to was assembled in preparation to the H&D Summer Academy 2022 | The mud-batteries how-to was assembled in preparation to the H&D Summer Academy 2022 and used during the workshop 'SoilPunk' | ||
Visit https://github.com/hackersanddesigners/Soilpunk_joulethief for more complete documentation. | Visit https://github.com/hackersanddesigners/Soilpunk_joulethief for more complete documentation. | ||
Revision as of 21:55, 11 July 2023
... looking back:
✧˖°. Mud batteries ⋆ ˚。⋆୨୧˚
How-to make batteries from soil
Collecting mud for the battery
Look for reddish brown soil (rich in iron) near river beds and swamps, areas where water has a reddish color. Preferably collect deep samples not from the surface.
About 1 liter makes 2 batteries. Ideally you get it a few days before the workshop, but it should be fine for up to two weeks. It is always good to collect more mud than what you calculate, in case some spill during preparations.
Make sure you take mud as well as some water (see image below).
Tools
- Pot and stove to cook the agar mixture
- Multimeter
- Clippers and wire stripper
- Breadboard
- Kitchen scale
- Liquids measuring cup
- Tape (or anything to mark different wires)
Materials
- Mud
- Containers with wide opening on top (ex: glass jar or plastic container - around 1L)
- Electric wires (Copper wires 30 cm - 2 wires are needed per battery)
- Stainless steel grids to be cut in rectangles. Size : around 8 x 8 cm, but can change according to the size and shape of your container. Aluminium nets are good to use but they are less conductive. You can use also kitchen strainer mesh. You can also experiment with the size of the net, for example: making it like a strip 8 x 20, to have more surface area. In this case you can roll it without making the surfaces touch.
- Epoxy glue
- Small brush to spread the glue
- Active coal
- Agar (10g is needed per 1L battery)
- Salt substances (any broth powder - 1 pack, 2g per battery). Broth powder is the one you use for cooking. We used the veggie broth cubes that you buy from the supermarket.
- LED
- Drinking Water
Making the Cathodes
To make the cathodes you need the active coal, epoxy glue, metal nets and electric wires.
- Empty the pills of the active coal to get the powder out, and place it on a sheet. (about 10 pills powder per 1 cathode disc)
- Cut two meshes in a rectangular shape 8 x 8cm. Place them in opposite directions and fold the edges so they are attached. We make two layers so it can hold the glue and coal well.
- Brush the glue on the mesh and make sure that you add enough glue and that it is brushed evenly on the surface of the mesh.
- Cover the brushed mesh with the active coal powder and press it very well. After pressing, add coal and press again. It is very important that the coal is covering the whole surface.
- After making sure that the mesh is covered and pressed with coal, connect the mesh from one of the sides to an electric wire. At the end you might need to bend the mesh to fit your container. Bend it, but be sure not to make the edges touch each other. More coal surface is better! Now leave it to fully dry.
Preparing first part of the Soil Battery
For this step you need the container (glass jar), mud, the dried cathodes.
- Put the cathode in the container (make sure that the glue dried and the coal is stuck to it).
- Fill the jar with mud so it covers the cathode, keeping the wire out of the container.
- Mark the wire with tape to identify that its negative. (black = negative)
- Hit the container to get all the trapped air bubbles out. It is VERY IMPORTANT to release the air bubbles from the mud.
Making the proton exchange membrane
Connecting the batteries in parallel
The water part in the battery is (+) and the mud part is (-). When connecting two batteries in parallel the (-) from the first battery should be connected to the (-) in the second one, and the (+) from the first to the (+) in the second. Then the (-) and (+) should be connected together to close the circuit. See the drawing:
The mud-batteries how-to was assembled in preparation to the H&D Summer Academy 2022 and used during the workshop 'SoilPunk' Visit https://github.com/hackersanddesigners/Soilpunk_joulethief for more complete documentation.